Today marks the first day of National Women’s History Month.
To celebrate, we’re celebrating women whose ideas, tenacity and inventions changed automotive history and the way we drive our cars:
Bertha Benz | Brake pads and the first road trip
Let’s start with the woman who put automobiles on the map.
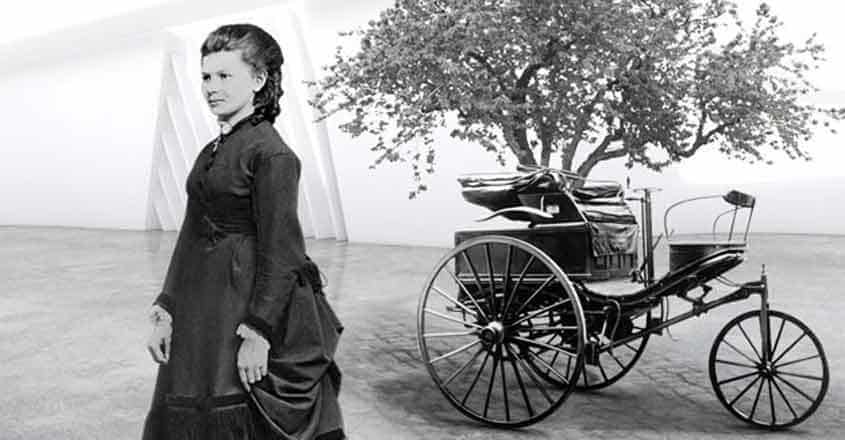

Bertha Benz was born in 1849 in Germany when women were denied access to higher education. She married young engineer, Carl Benz, and supported his numerous career paths, emotionally and financially, including the invention of the automobile.

No one was very interested in his motorcar, until Bertha and their sons took a now-famous road trip. Without Carl’s knowledge, Bertha and the boys snuck the car out of Carl’s workshop and took it on the first-long-distance road trip, from Mannheim to Pforzheim.
It was a rough ride on roads built for horses and carriages. She made several repairs during her journey and even invented the first brake pad, made of leather, when the car’s wooden brakes failed.
Her tenacity and determination created the popularity the Motor Car needed to become the world’s most important modern advancements.
Margaret Wilcox | Car heater
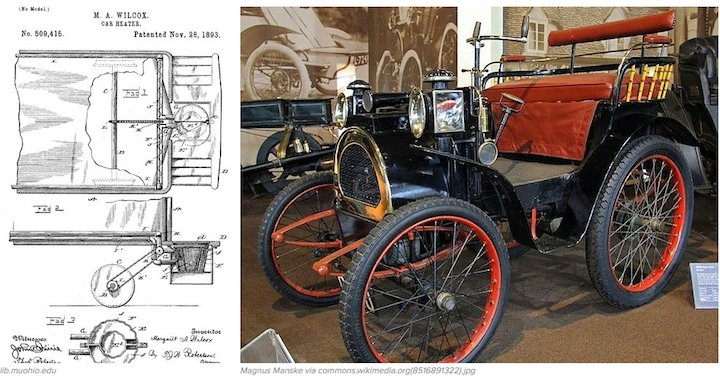
Margaret Wilcox was a trailblazer. Born in 1838, she was one of the very few female engineers of the time. In 1893, she received the patent for the interior car heater when she engineered a system that pulled the heat from the engine into the cab.
Wilcox’s work inspired the air heaters found in today’s cars making our cold winter drives more enjoyable.
Mary Anderson & Charlotte Bridgwood |Windshield wiper
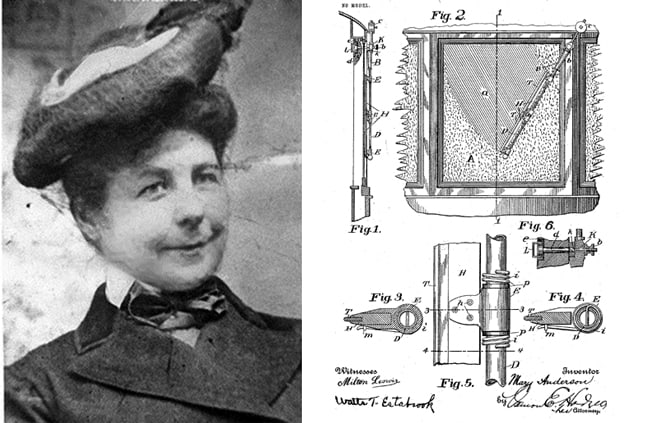
We have both Mary Anderson and Charlotte Bridgwood to thank for our windshield wipers that help us to drive safely in rain and snow.
Anderson’s idea for the windshield wiper came to her while riding on a trolley car to New York City in 1903. Due to the snowy weather, she couldn’t look out the window and enjoy the sights, and the driver had to stop constantly to wipe the snow off the windshield.

Inspired by her less-than-ideal road trip, she designed a spring-loaded arm with a rubber blade that would wipe across the windshield and could be activated from inside the car. Building on Anderson’s idea just a few years later, in 1917, Bridgwood upgraded the wiper to be electrically operated, her design used rollers instead of blades to clean a windshield.
Anderson and Bridgwood were too smart for their time because their patents expired after not getting enough attention from automakers. Little did they know windshield wipers would eventually become a standard feature in all cars.
Florence Lawrence | Auto signaling arms
At one point in automotive history, brake lights and turn signals didn’t exist – until silent-film actress Florence Lawrence saw the need.

In 1913, Lawrence invented a device called the Auto Signaling Arm that, “when placed on the back of the fender, can be raised or lowered by electrical push buttons,” she described.
When you pressed on the brake, the signaling arm would raise, indicating a stop.
Lawrence never received any patents for her design, but her idea inspired the necessary turn signals and brake lights we have today.
June McCarroll | Road markings
In 1917, while driving her Ford Model T down a California roadway, June McCarroll was inspired to create a safety measure that saves lives to this day:
“My Model T Ford and I found ourselves face to face with a truck on the paved highway,” she explained. “It did not take me long to choose between a sandy berth to the right and a ten-ton truck to the left! Then I had my idea of a white line painted down the center of the highways of the country as a safety measure.”
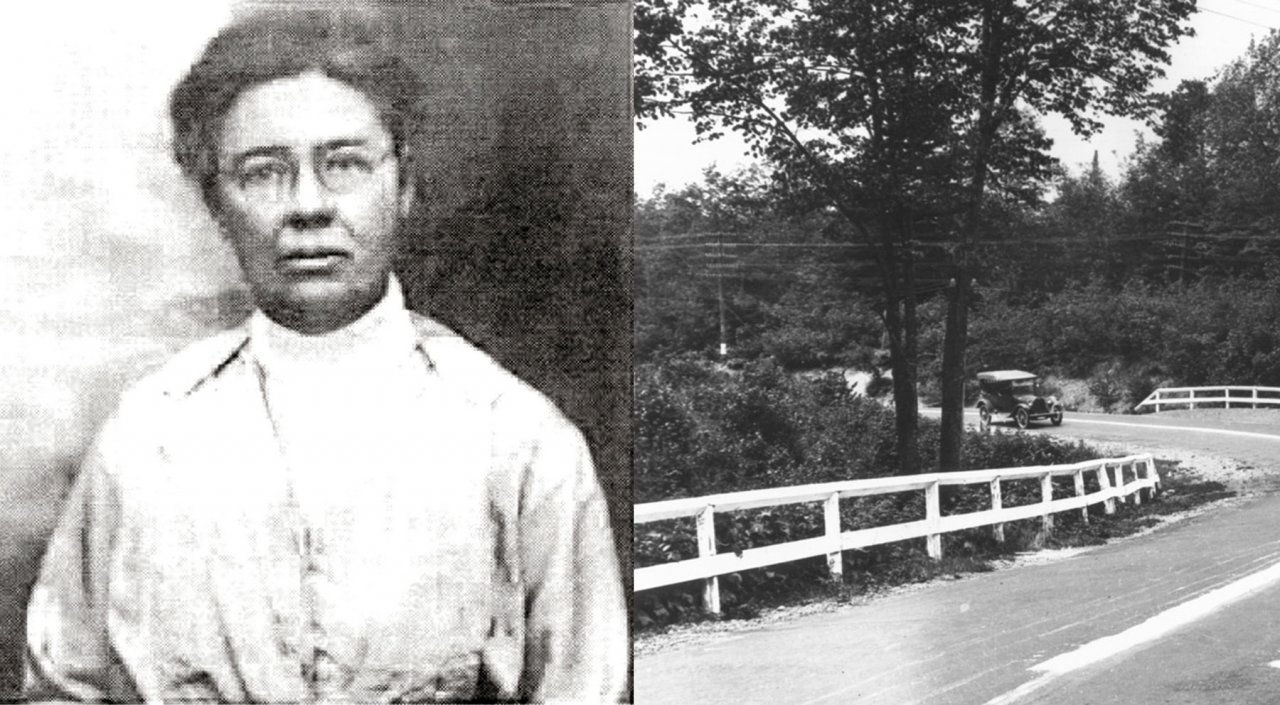

McCarroll launched a letter-writing campaign that gained so much attention that painted lines became California law in 1924. The rest of the country quickly followed.
Katharine Blodgett | Nonreflective glass
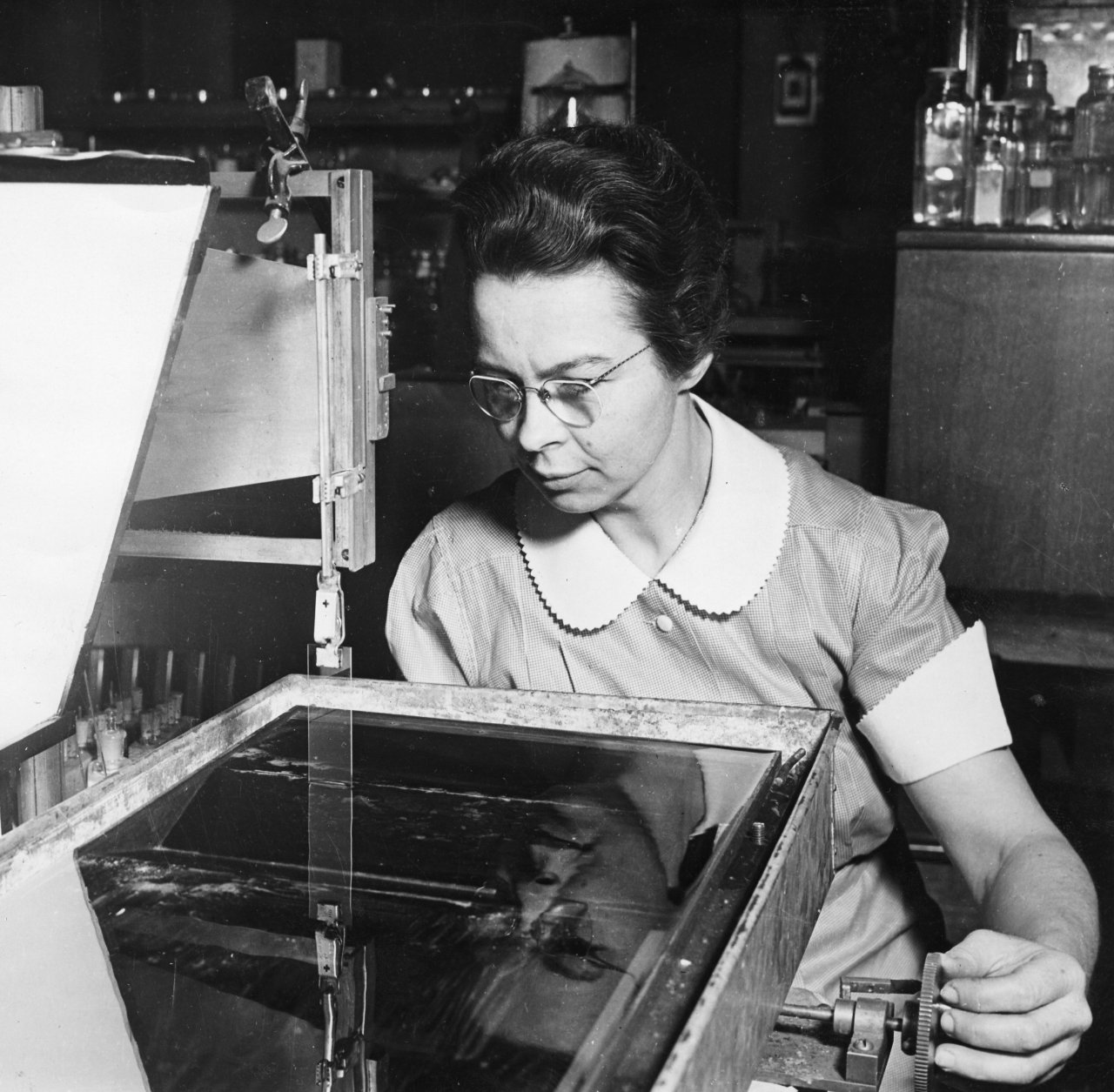

Engineer and scientist Katharine Blodgett is who we have to thank for creating non-reflective and anti-glare windshields.
Born in Schenectady, New York, in 1898, she obtained her bachelors degree at Bryn Mawr College and her masters at the University of Chicago. In 1926, at age 21, Blodgett was the first woman to receive a PhD in Physics at Cambridge University.
In 1938, she developed a liquid soap that, when 44 layers were spread over glass, would allow 99 percent of light to pass through. Her development paved the way for future engineers to create a more durable coating that wouldn’t wipe off.
Hedy Lamarr | Bluetooth
You might recognize Hedy Lamarr from the World War II film The Conspirators, but Lamarr was more than an actress – she was the inventor who created the technology in car’s Bluetooth features.
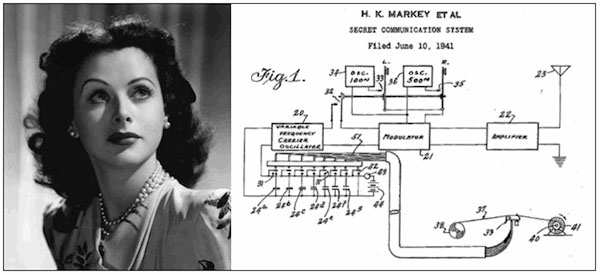
In the 1940s, Lamarr invented a device that blocked enemy ships from interrupting torpedo guidance signals. The device would take the torpedo signals and make them jump from frequency to frequency, making it near impossible for an enemy to locate the message.
It’s this ‘frequency jumping’ technology we find in the Bluetooth features in our car letting us talk on the phone hands-free or stream our favorite music.
Her technology can also be found in cell-phones, Wi-Fi and GPS.
Stephanie Kwolek | Kevlar tires and reinforced brake pads
In 1964 chemist Stephanie Kwolek discovered the synthetic fiber, Kevlar. This polymer fiber is five times stronger than steel but lighter than fiberglass. It’s even bulletproof.
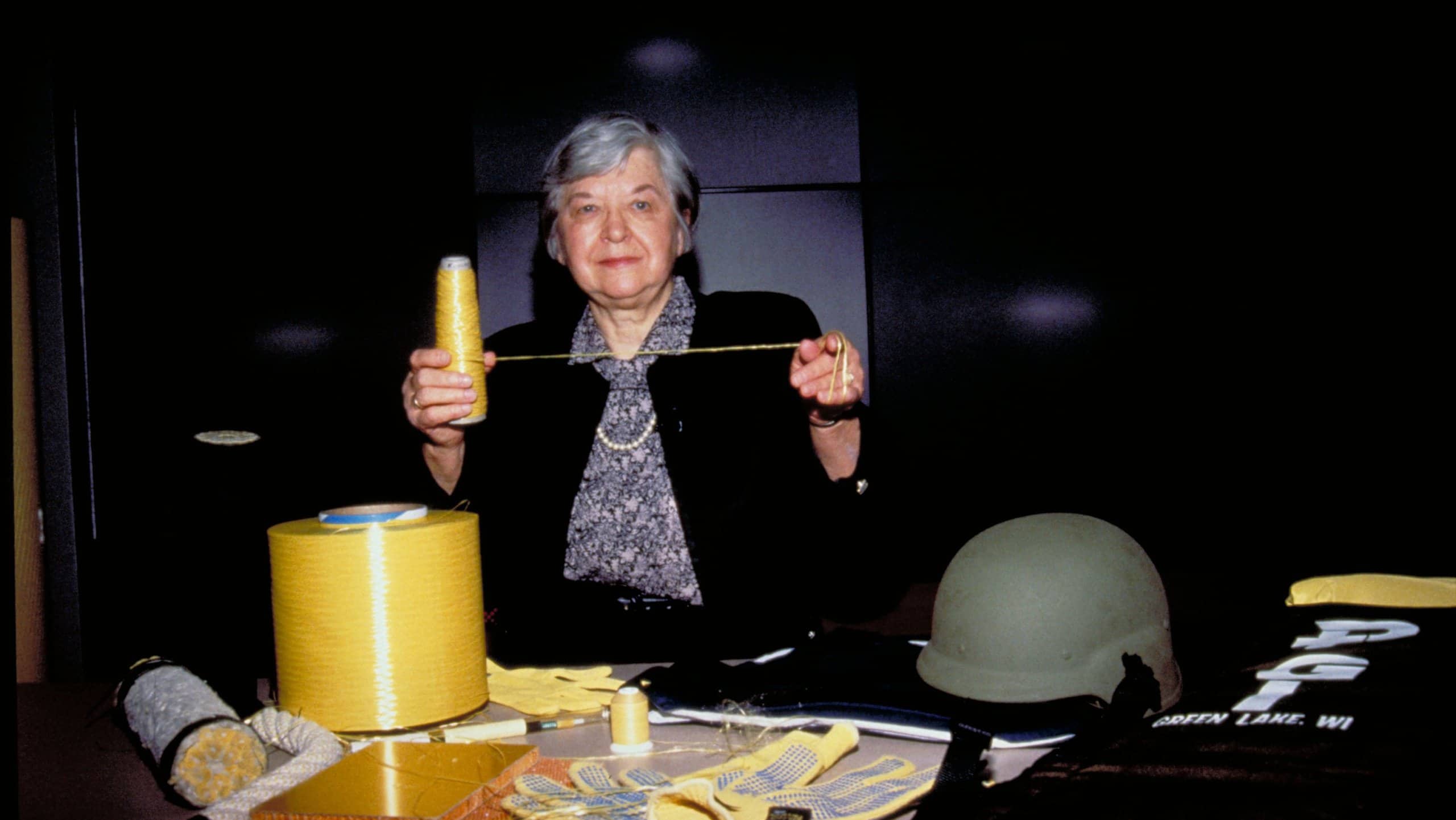

Her discovery has saved countless lives as Kevlar is now used to make bulletproof vests and armor.
Today, we can find Kevlar in our tires and in reinforced brake pads.
Mimi Vandermolen | Ergonomic controls
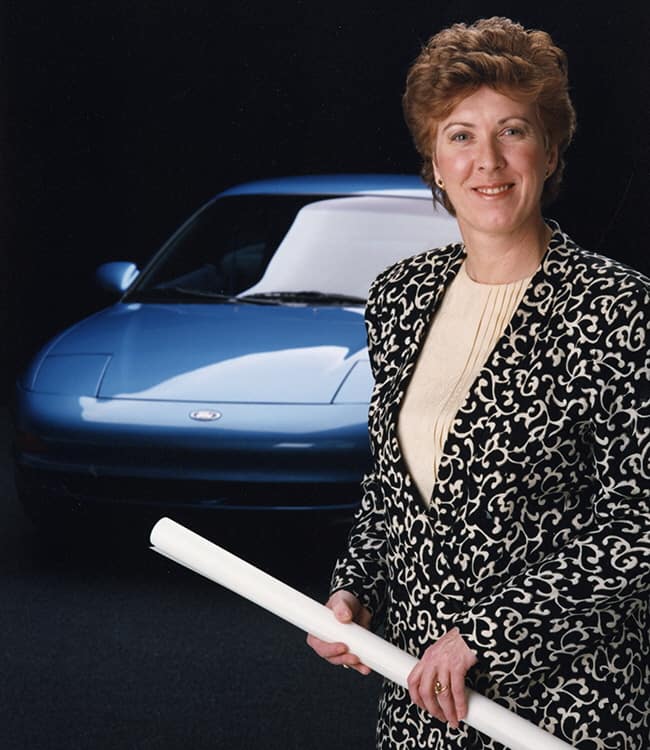

In 1970, Ford’s Design Studio welcomed Mimi Vandermolen to the team as one of the first full-time female designers.
After her first project working on the 1974 Mustang II, she led the design team for the 1986 Taurus interior.
In the Taurus, Vandermolen created ergonomic controls, dials for climate function, buttons with raised bumps, and a curved dash to make it easier to reach controls. Her work made the car more accessible and accommodating to drivers.
She went on to lead all of Ford’s North American small-car designs and the styling of the 1993 Probe, inside and out.
Gladys Mae West | GPS
As a mathematician who worked for the U.S. Naval Weapons Laboratory, Glady Mae West was the project manager for SEASAT, the first earth-orbiting satellite measuring ocean depths.
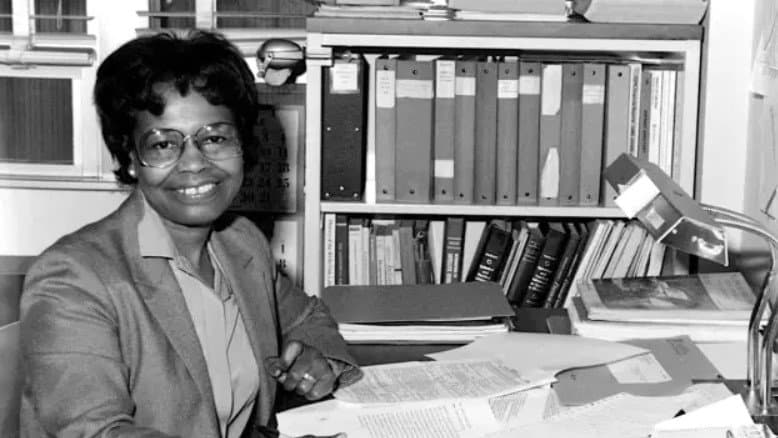

The work on the 1978 SEASAT project helped West and her team build the GEOSAT satellite creating computer simulations of earth’s surfaces.
Her calculations and work on the SEASAT and GEOSAT helped make the GPS systems in our cars – we’d be lost without her.






Thanks for a great article! We have learned so much from this. It is great to see the woman applying their talents in the auto industry. People are always amazed when I tell the Bertha Benz story. Again, thanks for a great piece.
Thank you Mike! I’m glad you enjoyed it. Bertha’s story is pretty spectacular. Cheers to all the hardworking women in the auto industry and beyond.
Nice story but Katharine Blodgett would have attended Bryn Mawr, not Bryn Mary. Also the photo of the lady in the Margaret Wilcox section is questionable. The woman pictured is in her late 20 or early 30s. Miss Blodgett would have been that age during the Civil War and I doubt women had bouffant hair dos in those days.
Thanks Thomas! Great feedback :).
Great job ladies !!
This article shines a well deserved light on the women of the industry.
You might like to read up on Alice H. Ramsey. I have an autographed copy of her book-“Veil, Duster and Tire Iron” and met her personally. An amazing person and definitely a pioneer in automotive history.
She is definitely an icon! I haven’t had a chance to read her book yet but would love to.
I so enjoyed your article, I shared it with many ladies in my life . . . thank you for writing it!
Please correct the major error in the first sentence.
Bertha Benz was born in 1849.
Otherwise, very good article.
Thank you.
Very interesting read. Thanks Racheal!
Great article! It’s great to read about all these women’s work and original ideas that paved the way in the automobile through today. This proves the love for automobiles is not just for men. Thanks for writing this article.
Thank you for the women’s history article. I am forwarding it to my Great niece!
As the son of a Mechanical Engineer (my mother who graduated from London “red brick” university with a Doctorate in Fluid and Thermo dynamics) and an Electrical Engineer (my Father who graduated from Cape Town university and was a specialist in high voltage power transmission), I had a very well cultured respect for Woman who bravely venture into Engineering, specifically Mechanical.
As a “gearhead” and an Electrical Engineer, any article showing how dedicated female engineers are, intrigues me.
Thanks you for your insight !